Understanding numbers can sometimes feel like a daunting task, but calculating the mean is simpler than you might think. The mean, often referred to as the average, provides valuable insights into sets of data by summarizing large amounts of information into a single figure. Whether you’re analyzing test scores or tracking expenses, knowing how to calculate mean can empower you in making informed decisions.
In this guide, we’ll break down the process step-by-step so that anyone can master it with ease. By the end of this article, you’ll not only know how to find the average but also appreciate its significance in everyday life. Ready to dive into the world of averages? Let’s get started!
What is the Mean?
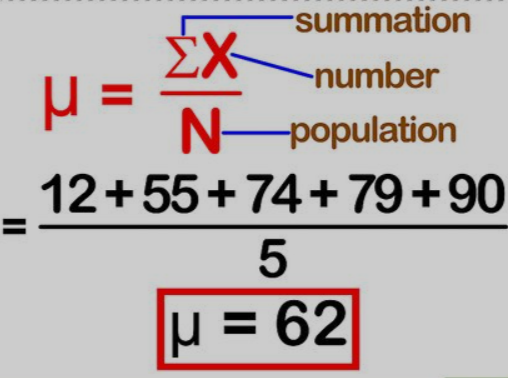
The mean, often called the average, is a statistical measure that represents the central point of a data set. It gives you an idea of where most values lie within that set.
To find the mean, you add up all individual numbers and then divide by how many values there are. This simple calculation turns complex data into something easily understandable.
In practical terms, the mean helps to distill information down to one representative number. This can be especially useful when comparing different sets or understanding trends over time.
While it’s just one way to summarize data, it plays a crucial role in statistics and everyday decision-making. Understanding this concept opens doors to better insights and informed choices across various contexts.
Why is the Mean Important?
The mean serves as a fundamental statistical measure, providing a simple way to understand data sets. It helps in summarizing large amounts of information into one value that represents the entire group.
In research and analysis, the mean assists in revealing trends and patterns. This gives insights into behaviors or outcomes across various disciplines, from economics to education.
Businesses also rely on the mean for decision-making. Understanding average sales or customer satisfaction scores can influence strategies and improve performance.
Moreover, the mean is crucial in comparing different data sets. It allows analysts to assess disparities between groups effectively.
Education often uses the mean to evaluate student performance. Teachers gauge overall class understanding through averages on tests or assignments.
By grasping why calculating the mean matters, you unlock deeper insights hidden within your data.
Step 1: Gather Data
Gathering data is the first crucial step in calculating the mean. Before crunching numbers, you need a clear set of values to work with.
Start by identifying what you want to measure. This could be anything from test scores to daily temperatures or even sales figures. The more relevant your data, the better your results will be.
Next, decide how you’ll collect this information. You can use surveys, databases, or even gather it manually if necessary. Just ensure that your method produces accurate and complete data.
Once you’ve compiled everything, take a moment to organize it neatly—whether that’s on paper or digitally. A well-structured dataset makes subsequent steps much easier and minimizes errors later on when you’re ready for calculations.
Step 2: Add Up all the Numbers
Once you have gathered your data, it’s time to dive into the fun part: adding up all the numbers. This step is crucial for calculating the mean accurately.
Start with a clear list of your values. Whether they are test scores, survey results, or any other type of numerical data, make sure everything is visible.
Use a calculator if necessary. It helps avoid simple mistakes that can derail your final result. You want precision here; every number counts.
Begin adding from one end to the other—left to right or vice versa—the choice is yours! Just maintain consistency throughout this process.
If you’re handling larger datasets, consider grouping numbers together in pairs for easier addition. This can simplify things and minimize errors as you progress through your calculations.
Once you’ve summed everything up, you’ll be ready for the next step in finding the mean!
Step 3: Count the Total Number of Values
Counting the total number of values is a crucial part of calculating the mean. This step ensures that you know exactly how many data points you’re working with.
Start by reviewing your gathered data. Each individual value contributes to the overall average, so accuracy matters here.
Simply tally each entry in your dataset until you’ve accounted for all numbers. You can use a notepad or digital tool; whichever allows for easy counting will work.
Make sure there are no duplicates unless they are part of your original dataset. A common mistake is overlooking certain entries, which can skew your final result.
Double-checking this count safeguards against errors and sets a solid foundation for the next steps in finding the mean. Getting it right now saves time later on and enhances clarity in calculations ahead!
Step 4: Divide the Sum by the Total Number of Values
Now that you have the total sum of your data, it’s time for the final step in finding the mean. This is where division comes into play.
Take your total sum and divide it by the number of values you counted earlier. This simple mathematical operation gives you a single value: the average or mean.
For example, if your total was 50 and you had five numbers, dividing 50 by 5 results in an average of 10. It’s straightforward but crucial for understanding what this average represents about your dataset.
This calculation transforms all those individual numbers into one meaningful figure that reflects them collectively. It’s like distilling a complex mixture down to its essence—a clear representation that can inform decisions or analyses going forward.
Example Calculation and Explanation
Let’s look at a practical example to make sense of calculating the mean. Imagine you have five test scores: 85, 90, 78, 92, and 88.
First, add these numbers together. The sum is 433.
Next, count how many values there are. In this case, it’s five test scores.
Now comes the key step: divide the total sum by the number of values. You take that sum of 433 and divide it by 5.
The result? A mean score of approximately 86.6. This tells you what your average performance looks like across those tests.
Understanding this process helps in various situations beyond academics too! Whether you’re assessing data for a project or simply evaluating personal achievements, knowing how to calculate mean provides insight into overall trends and averages.
Practical Applications of Finding the Mean
Finding the mean has practical applications across various fields. In education, teachers often calculate the average score of students to determine overall performance. This helps in identifying areas where additional support may be needed.
Business analysts use the mean to assess sales data, providing insights into customer behavior and market trends. By examining average sales figures, companies can make informed decisions about inventory and marketing strategies.
In healthcare, researchers frequently analyze patient outcomes by calculating means from clinical trials. This information is vital for understanding treatment effectiveness.
Sports statistics also rely on mean calculations to evaluate player performance over a season. Coaches and managers use this data to make strategic decisions regarding team composition.
From daily life budgeting to scientific research, knowing how to calculate the mean empowers individuals and organizations alike with valuable insights that drive better decision-making.
Common Mistakes in Calculating the Mean
Calculating the mean seems straightforward, but common pitfalls can lead to errors. One frequent mistake is forgetting to include all data points. If even one number is omitted, the mean will be inaccurate.
Another issue arises when people miscount the total number of values. It’s crucial to ensure that every entry in your dataset is accounted for before performing any calculations.
Using incorrect formulas can also trip you up. The formula for calculating the mean is simple: sum all numbers and divide by the count of those numbers. Deviating from this method leads to confusion.
Relying solely on memory instead of writing down values may result in oversights or inaccuracies. Recording your data helps maintain clarity and reduces mistakes during calculation. Always double-check your work to ensure accuracy!
Conclusion
Finding the mean is a straightforward process that provides valuable insights into your data set. By understanding how to calculate the mean, you can effectively summarize large amounts of information and make informed decisions based on averages. Whether you’re analyzing test scores, sales figures, or any other numerical data, knowing how to determine the mean helps you grasp trends and patterns.
Common pitfalls include forgetting to count all values or making errors in addition. By being mindful of these mistakes and following each step closely, you’ll enhance both accuracy and confidence in your calculations.
The ability to calculate the mean is not just beneficial for academic purposes; it has practical applications across various fields including business analytics, social sciences, healthcare statistics, and more. Embracing this skill allows you to extract meaningful conclusions from your data effortlessly.
With practice and application of these steps—gathering data, adding numbers together accurately, counting values correctly, then dividing—you’ll become proficient at calculating means in no time. Keep exploring how averages influence decision-making processes around you!